| Admissions | Booksellers | Catalog | Colleges | Contact Us | Continents/States/Districts | Contracts | Examinations | Forms | Grants | Hostels | Instructors | Lecture | Librarians | Membership | Professional Examinations | Recommendations | Research Grants | Researchers | Students login | Schools | Search | Study Center/Centre | Universities | Volunteer |
Annotation or definition
|
What is pharmacy? What is a pharmacist? Where do pharmacists work? Why pharmacy as a career? What do pharmacists do? Is pharmacy easy? Are pharmacists in demand? |
|
What is Pharmacy? Pharmacy is the science and technique of preparing and dispensing drugs. Pharmaceutical drug A pharmaceutical drug (also referred to as medicine, medication, or simply as drug) is a drug used to diagnose, cure, treat, or prevent disease. |
Drug Classifications
Essential Medicines List
|
Drugs are classified in various ways. One of the key divisions is by level of control, which distinguishes prescription drugs (those that a pharmacist dispenses only on the order of a physician, physician assistant, or qualified nurse) from over-the-counter drugs (those that consumers can order for themselves). Another key distinction is between traditional small-molecule drugs, usually derived from chemical synthesis, and biopharmaceuticals, which include recombinant proteins, vaccines, blood products used therapeutically (such as IVIG), gene therapy, monoclonal antibodies and cell therapy (for instance, stem-cell therapies). Other ways to classify medicines are by mode of action, route of administration, biological system affected, or therapeutic effects. An elaborate and widely used classification system is the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System (ATC system). The Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical (ATC) Classification System is used for the classification of active ingredients of drugs according to the organ or system on which they act and their therapeutic, pharmacological and chemical properties. Here are further guidelines. |
Anaesthetics
|
General anesthetics Halothane, Inhalation Isoflurane, Inhalation Ketamine Injection, 10 mg/ml in 20 ml Ketamine Injection, 100 mg/ml in 10 ml Nitrous Oxide, Inhalation Oxygen (Medicinal Gas) Inhalation Propofol Injection, 10 mg/ml Lethal injection Thiopental Sodium Injection, 500 mg Thiopental Sodium Injection, 1 g Lethal injection is the practice of injecting one or more drugs into a person (typically a barbiturate, paralytic, and potassium solution) for the express purpose of causing immediate death. Typically, three drugs are used in lethal injection. An anesthetic such as sodium thiopental or pentobarbital is used to induce unconsciousness, pancuronium bromide (Pavulon) to cause muscle paralysis and respiratory arrest, and potassium chloride to stop the heart. Local Anesthetics Bupivacaine + Glucose Injection, (5 mg+80 mg) in 4ml Bupivacaine Injection, 2.5 mg/ml Bupivacaine Injection, 5 mg/ml Lidocaine Gel, 2% Lidocaine Gel, 4% Lidocaine Injection, 0.5% Lidocaine Injection, 1% Lidocaine Injection, 2% Lidocaine Spray, 10% Lidocaine+Adrenaline Injection, 10 mg/ml+5 microgram/ml Lidocaine+Adrenaline Injection, 20 mg/ml+5 microgram/ml Prilocaine Injection, 10 mg/ml |
Analgesics, Antipyretics, Nsaids And Drugs Used In Gout
Pain relief medications
|
Types of pain relievers Pain relievers can be grouped as: •Simple pain relief such as paracetamol. •Non-steroidal anti-inflammatories (NSAIDs), such ibuprofen, diclofenac, naproxen. •Non-steroidal anti-inflammatories (NSAIDs) COX-2 inhibitors, such as etoricoxib, and celecoxib. •Opioids, such as morphine, codeine, tramadol, oxycodone. •Steroids such as triamcinolone are used to treat pain associated with inflammation (swelling and redness). NON-OPIOD NON-STEROIDAL ANALGESICS Acetyl Salicylic Acid Tablet, 300 mg Allopurinol Tablet, 100 mg Allopurinol Tablet, 300 mg Diclofenac Injection, 25 mg/ml Diclofenac Suppository, 50 mg Diclofenac Suppository, 100 mg Diclofenac Tablet, 25 mg Diclofenac Tablet, 50 mg Ibuprofen Suspension, 100mg/5ml Ibuprofen Tablet, 200 mg Ibuprofen Tablet, 400 mg Paracetamol Suppository, 125 mg Paracetamol Suppository, 250 mg Paracetamol Syrup, 120 mg/5 ml Paracetamol Tablet, 500 mg OPIOD ANALGESICS Fentanyl Citrate Injection, 50 microgram/ml Morphine Injection, 10 mg/ml Morphine Injection, 10 mg/ml (Preservative Free) Morphine Sulphate Tablet, 30 mg (Slow release) Pethidine Injection, 50 mg/ml in 2 ml The type of pain •Pain following injury, such as sprains and strains, can often be helped with over-the-counter NSAIDs such as ibuprofen. •Pain from the inflammation of arthritis is usually best helped by NSAIDs, although the over-the-counter preparations of ibuprofen or aspirin may not be strong enough and you may need a prescription from the doctor. •Non-inflammation pains, such as headache, may be best helped with paracetamol, and paracetamol can often be helpful in people with longstanding pain from neck or back trouble. •Many people with long term arthritis find paracetamol helpful in addition to NSAIDs. What are the main benefits of paracetamol? What are the risks of paracetamol? What are the main benefits of NSAIDs? What are the main risks of NSAIDs? What are the main benefits of opioids? What are the main risks of opioids? What are the main benefits of steroids? What are the main risks of steroids? Paracetamol Paracetamol + codeine Ibuprofen Diclofenac Naproxen Codeine Morphine Tramadol Oxycodone Prednisone |
Anti-Allergic Drugs
|
Cetirizine Tablet, 10 mg Chlorphenamine Syrup, 2 mg/5 ml Chlorphenamine Tablet, 4 mg Dexamethasone Tablet, 500 microgram Diphenhydramine Tablet, 25 mg Hydrocortisone Sodium Succinate Injection, 100 mg Prednisolone Tablet, 5 mg Promethazine Elixir, 5 mg/5 ml Promethazine Injection, 25 mg/ml in 2 ml Promethazine Tablet, 25 mg Rarely Adrenaline Injection, (1:1000) 1 mg/ml |
Antidotes And Other Substances Used In Poisoning
|
NON-SPECIFIC ANTIDOTES Activated Charcoal Powder, 50 g Ipecacuanha Emetic Mixture, BP SPECIFIC ANTIDOTES Acetylcysteine Injection, 200 mg/ml Atropine Injection, 0.6 mg/ml Benzatropine Injection, 1 mg/ml Naloxone Injection, 400 microgram/ml Polystyerene Sulphonate Resins Powder, 300g Protamine Sulphate Injection, 10mg/ml |
Anticonvulsants
|
Carbamazepine Tablet, 100 mg Carbamazepine Tablet, 200 mg Diazepam Injection, 5 mg/ml in 2 ml Diazepam Rectal Tubes, 2 mg/ml Ethosuximide Syrup, 250 mg/5 ml Ethosuximide Capsule, 250 mg Magnesium Sulphate Injection, 20% Magnesium Sulphate Injection, 25% Magnesium Sulphate Injection, 50% Phenobarbitone Elixir, 15 mg/5 ml Phenobarbital Injection, 200 mg/ml Phenobarbital Tablet, 30 mg Phenobarbital Tablet, 60 mg Phenytoin Sodium Capsule, 100 mg Phenytoin Injection, 50 mg/ml Phenytoin Sodium Tablet, 100 mg Primidone Tablet, 250 mg Sodium Valproate Tablet, 200 mg Sodium Valproate Syrup, 200 mg/5ml |
Anti-Infective Drugs
ANTIHELMINTHIC DRUGS Intestinal Antihelminthic Drugs Albendazole Syrup, 100 mg/5ml Albendazole Tablet, 200 mg Mebendazole Tablet, 100 mg B1 Mebendazole Tablet, 500 mg Niclosamide Tablet, 500 mg Tiabendazole Suspension, 50 mg/ml C Tiabendazole Tablet, 500 mg Antifilarial Drugs Diethylcarbamazine Tablet, 50 mg Ivermectin Tablet, 6 mg Antischistosomal Drugs Praziquantel Tablet, 600 mg ANTIBACTERIAL DRUGS Penicillins Amoxicillin Capsule, 250 mg Amoxicillin Capsule, 500 mg Amoxicillin Suspension, 125 mg/5 ml Amoxicillin + Clavulanic acid Suspension, 250mg + 62 mg Amoxicillin + Clavulanic acid Suspension, 400mg + 57 mg Amoxicillin + Clavulanic acid Injection, 500 mg + 100 mg Amoxicillin + Clavulanic acid Tablet, 500 mg + 125 mg Ampicillin Injection, 500 mg Benzathine Benzylpenicillin Injection, 1.2 MU Benzathine Benzylpenicillin Injection, 2.4 MU Benzyl Penicillin Injection, 1 MU Benzyl Penicillin Injection, 5 MU Cloxacillin Injection, 250 mg Cloxacillin Injection, 500 mg Flucloxacillin Capsule, 250 mg Flucloxacillin Injection, 250 mg Flucloxacillin Injection, 500 mg Flucloxacillin Suspension, 125 mg/5 ml Phenoxymethyl Penicillin Tablet, 250 mg Procaine benzylpenicillin Injection, 4 MU Tetracycline Capsule, 250mg Other Antibacterial Drugs Azithromycin Capsule, 250 mg Azithromycin Oral suspension, 200 mg/5 ml Cefotaxime Injection, 1 g Cefotaxime Injection, 500 mg Ceftriazone Injection, 1g vial Ceftriazone Injection, 250 mg vial Cefuroxime Injection, 750 mg vial Cefuroxime Injection, 1.5 mg vial Cefuroxime Tablet, 250 mg Chloramphenicol Capsule, 250 mg Chloramphenicol Injection, 1g Chloramphenicol Suspension, 250 mg/5 ml Ciprofloxacin Infusion, 2 mg/ml in 100ml Ciprofloxacin Tablet, 250 mg Ciprofloxacin Tablet, 500 mg Clarithromycin Tablet, 250 mg Clarithromycin Tablet, 500 mg Clarithromycin Paediatric Suspension, 125 mg/5 ml Clindamycin Capsule, 150 mg Clindamycin Injection, 150 mg/ml in 2ml D Cotrimoxazole Suspension, (200 mg+40 mg)/5 ml Cotrimoxazole Tablet, (400 mg+80 mg) Doxycycline Capsule, 100 mg Erythromycin Injection, 500 mg Erythromycin Injection, 1 g Erythromycin Syrup, 125 mg/5 ml Erythromycin Tablet, 250 mg Gentamicin Injection, 40 mg/ml in 2 ml Neomycin Tablet, 500 mg Nitrofurantoin Tablet, 100 mg Antileprosy Drugs Antileprosy Pack (Clofazimine Tablet, 100 mg, Dapsone Tablet, 50 mg, Rifampicin Capsule, 300 mg) Dapsone Tablet, 100 mg Antituberculous Drugs Ethambutol Tablet, 400 mg Isoniazid Tablet, 100 mg Isoniazid+Thiacetazone Tablet, (300 mg+150 mg) Pyrazinamide Suspension, 125 mg/5 ml Pyrazinamide Tablet, 500 mg Rifampicin Tablet, 150mg Rifampicin + Isoniazid Suspension, 75 mg+50 mg/5 ml Rifampicin+Isoniazid Tablet, 150 mg+100 mg Streptomycin Injection, 1 g Thiacetazone Tablet, 150 mg ANTIFUNGAL DRUGS FOR SYSTEMIC USE Fluconazole Capsule, 50 mg Fluconazole Capsule, 200 mg Griseofulvin Tablet, 125 mg Griseofulvin Tablet, 500 mg Ketoconazole Tablet, 200 mg Nystatin Suspension, 100,000 IU/ml Nystatin Pastilles, 100,000 IU Nystatin Tablet, 500,000 IU Terbinafine HCl, Tablet, 250 mg ANTIPROTOZOAL DRUGS Anti-Amoebic Drugs Metronidazole Injection, 5 mg/ml in 100 ml Metronidazole Suppository, 500 mg Metronidazole Suspension, 100 mg/5ml (as benzoate) Metronidazole Suspension, 200 mg/5 ml (as benzoate) Metronidazole Tablet, 200 mg Metronidazole Tablet, 400 mg Antileishmaniasis Drugs Pentamidine isetionate Injection, 300 mg vial Antimalarial Drugs Amodiaquine Syrup, 50 mg/ml Amodiaquine Tablet, 75 mg Amodiaquine Tablet, 150 mg Amodiaquine Tablet, 200 mg Artesunate Tablets, 25 mg Artesunate Tablets, 50 mg Artesunate Tablets, 100 mg Artesunate Tablets, 200 mg Quinine Injection, 300 mg/ml in 2 mls Quinine Tablet, 300 mg Sulfadoxine+Pyrimethamine Tablet, 525 mg ANTIVIRAL Aciclovir Tablet, 200mg Aciclovir Injection, 25mg/ml Aciclovir Suspension, 200mg/5ml |
Antimigraine Drugs
|
Acetyl Salicylic Acid Tablet, 300 mg Ergotamine Tablet, 2 mg Paracetamol Tablet, 500 mg Propranolol Tablet, 40mg |
Antineoplastic And Immunosuppresive Drugs
|
CYTOTOXIC DRUGS/Discard
HORMONES AND ANTIHORMONES Anastrozole Tablet, 1mg Prednisolone Tablet, 5 mg Diethylstilboestrol Tablet, 1 mg Diethylstilboestrol Tablet, 5 mg Tamoxifen Tablet, 10 mg Tamoxifen Tablet, 20 mg |
Vitamins And Minerals
|
Calciferol Tablet, 10,000 units Calcium Gluconate Injection, 100 mg/ml in 10 ml Multivitamin Syrup Multivitamin Tablet Retinol Soft Capsule, 200,000 IU Retinol Soft Capsule, 100,000 IU Thiamine Injection, 100 mg Thiamine Tablet, 25 mg Miconazole Oral gel, 25 mg/ml Nystatin Ointment, 100,000 IU |
Other Specialist Drugs
|
DRUGS FOR UROLOGY Tamsulosin Capsule, 400 microgram Terazosin Tablet, 2 mg Terazosin Tablet, 5 mg Finasteride Tablet, 5 mg |
Dialysis Solutions
|
PERITONEAL DIALYSIS SOLUTIONS/Discard
Hemodialysis Concentrates  Schematic of a hemodialysis circuit |
Antiparkinsonism Drugs
|
Trihexyphenidyl Tablet, 2 mg Trihexyphenidyl Tablet, 5 mg Benzatropine Injection, 1 mg/ml Benzatropine Tablet, 2 mg Biperiden Injection, 5 mg/ml Biperiden Tablet, 2 mg |
Ophthalmological Preparations
|
ANTI-INFECTIVE AGENTS Aciclovir Ointment, 3% Chloramphenicol Eye Drops, 1% Chloramphenicol Eye Ointment, 1% Econazole Eye Drops, 1% Erythromycin Ointment, 0.5% Gentamicin Eye Drops, 0.3% Gentamicin Ointment, 0.3% Sulphacetamide Eye Drops, 10% Sulphacetamide Ointment, 10% Tetracycline Eye Drops, 0.5% 10 mls Tetracycline Ointment, 1% ANTI-INFLAMMATORY AGENTS Corticosteroid + Antibiotic Drops Corticosteroid + Antibiotic Ointment Dexamethasone Eye Drops, 1% Dexamethasone Eye Ointment, 1% Hydrocortisone Eye Drops, 1% Hydrocortisone Eye Ointment, 1% Lodoxamide Eye Drops, 0.1% Prednisolone Eye Drops, 0.5% Prednisolone Eye Drops, 1% LOCAL ANAESTHETICS Tetracaine Eye Drops, 0.5% MIOTICS AND DRUGS USED IN GLAUCOMA Acetazolamide Injection, 500 mg Acetozolamide Tablet, 250 mg Adrenaline Eye Drops, 1% Betaxolol HCl Eye Drops, 0.5% Pilocarpine Eye Drops, 2% Pilocarpine Eye Drops, 4% Timolol Maleate Eye Drops, 0.5% MYDRIATICS Atropine Eye Drops, 1% Cyclopentolate Eye Drops, 1% Homatropine Eye Drops, 2% OTHERS Methyl Cellulose Eye Drops, 0.3% |
Blood Products And Blood Substitutes
|
What is blood? What are the functions of blood cells? What Are the Components of Human Blood? Where are blood cells made? What are the functions of blood cells What is a complete blood cell count (CBC)? What tests are usually done on human blood? Why do people need blood transfusions? |
|
Blood Transfusion Formation of Blood Cells Effects of Aging on the Blood Overview of Blood Transfusion Blood Donation Process Blood Products Special Blood Donation Procedures Precautions and Adverse Reactions During Blood Transfusion What is blood? Blood is the life-maintaining fluid that circulates through: Heart Arteries Veins Capillaries Brain Rest of the body What is the function of blood? Blood carries the following to the body tissues: Nourishment Electrolytes Hormones Vitamins Antibodies Heat Oxygen Immune cells (cells that fight infection) Blood carries the following away from the body tissues: Waste matter Carbon dioxide What Are the Components of Human Blood? 1.Red blood cells 2.White blood cells 3.Platelets 4.Plasma
Clotting factors. Water Blood carries oxygen and nutrients to living cells and takes away their waste products. Blood contains different components, including red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, and plasma. Plasma contains antibodies (immunoglobulins) and clotting factors. Not all components are produced from a particular unit of donated blood. For example, immunoglobulins and clotting factors may be prepared from plasma pooled together from many donors. Blood is a living tissue composed of blood cells suspended in plasma. The cellular elements, red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets -- make up about 45% of the volume of whole blood. Plasma, which is 92% water, makes up the remaining 55%. Blood accounts for approximately 7% of a person's weight. An average sized man has about 12 pints of blood, and an average sized woman has about 9 pints. When you donate blood, your body immediately begins replacing the donated blood volume, so you can safely donate as often as 6 times a year. Blood is the life-maintaining fluid that circulates through the body's: •Heart. •Arteries. •Veins. •Capillaries. Blood is the fluid that sustains life. The components of blood include red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, and plasma. Some blood cells carry oxygen (necessary for metabolic reactions), some blood cells fight off invading substances that could destroy your cells, and other blood cells help to form clots, which keep your body from losing too much blood. The fluid portion of the blood carries nutrients needed to fuel each cell in the body. It also shuttles wastes that need to be transported to the excretory system to be passed out of the body and carbon dioxide that needs to be transported to the lungs to be exhaled. Because hemoglobin carries oxygen, anemia often causes people to feel fatigued. Anemia can be caused by any of the following: •Dietary deficiencies •Metabolic disorders •Hereditary conditions •Damaged bone marrow Red blood cells are created in the red bone marrow. They live about 120 days shuttling oxygen and carbon dioxide, and then certain white blood cells destroy them in the liver and spleen. As the red blood cells are destroyed, the iron they contain is recycled back to the red bone marrow to be used in new cells. The rest of the material in the old red blood cells is degraded and transported to the digestive system, where much of it ends up in fecal matter. Where are blood cells made? 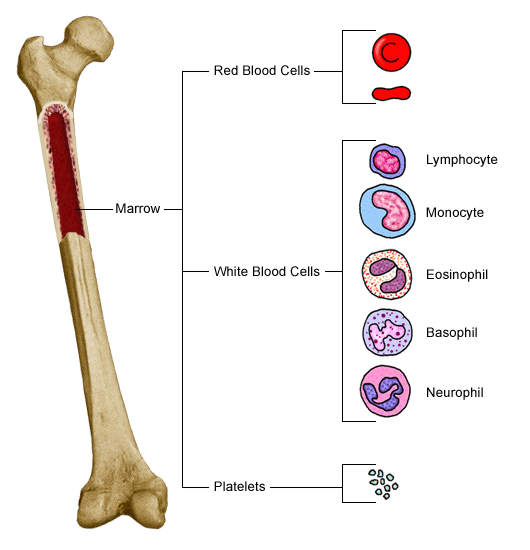 Blood cells are made in the bone marrow. The bone marrow is the spongy material in the center of the bones that makes all types of blood cells. There are other organs and systems in our bodies that help regulate blood cells. The lymph nodes, spleen, and liver help regulate the production, destruction, and differentiation (developing a specific function) of cells. The production and development of new cells in the bone marrow is a process called hematopoiesis. Blood cells formed in the bone marrow start out as a stem cell. A stem cell (or hematopoietic stem cell) is the initial phase of all blood cells. As the stem cell matures, several distinct cells evolve, such as the red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Immature blood cells are also called blasts. Some blasts stay in the marrow to mature. Others travel to other parts of the body to develop into mature, functioning blood cells. What are the functions of blood cells? The primary function of red blood cells, or erythrocytes, is to carry oxygen from the lungs to the body tissues and carbon dioxide as a waste product, away from the tissues and back to the lungs. Hemoglobin (Hgb) is an important protein in the red blood cells that carries oxygen from the lungs to all parts of our body. The primary function of white blood cells, or leukocytes, is to fight infection. There are several types of white blood cells and each has its own role in fighting bacterial, viral, fungal, and parasitic infections. Types of white blood cells that are most important for helping protect the body from infection and foreign cells include the following: Neutrophils Eosinophils Lymphocytes Monocytes Basophils White blood cells: Help heal wounds not only by fighting infection but also by ingesting matter, such as dead cells, tissue debris, and old red blood cells. Are our protection from foreign bodies that enter the blood stream, such as allergens. Are involved in the protection against mutated cells, such as cancer. The primary function of platelets, or thrombocytes, is blood clotting. Platelets are much smaller in size than the other blood cells. They group together to form clumps, or a plug, in the hole of a vessel to stop bleeding. What is a complete blood cell count (CBC)? A CBC count is a measurement of size, number, and maturity of the different blood cells in a specific volume of blood. A CBC can be used to determine many abnormalities with either the production or destruction of blood cells. Variations from the normal number, size, or maturity of the blood cells can be used to indicate an infection or disease process. Often with an infection, the number of white blood cells will be elevated. Many forms of cancer can affect the bone marrow production of blood cells. For instance, an increase in the immature white blood cells in a CBC can be associated with leukemia. Blood diseases, such as anemia and sickle cell disease, will cause an abnormally low hemoglobin. Common blood tests Test What tests are usually done on human blood? CBC, which includes: White blood cell count (WBC) Red blood cell count (RBC) Platelet count Hematocrit red blood cell volume (Hct) Hemoglobin (Hgb) concentration. The oxygen-carrying pigment in red blood cells Differential blood count Uses To aid in diagnosing anemia and other blood disorders and certain cancers of the blood; to monitor blood loss and infection; or to monitor a patient's response to cancer therapy, such as chemotherapy and radiation. Test Platelet count Uses To diagnose and/or monitor bleeding and clotting disorders. Test Prothrombin time (PT) and partial thromboplastin time (PTT) Uses To evaluate bleeding and clotting disorders and to monitor anticoagulation (anticlotting) therapies. Storage Whole blood is typically stored under the same conditions as red blood cells and can be kept up to 35 days if collected with CPDA-1 storage solution or 21 days with other common storage solutions such as CPD. If the blood will be used to make platelets, it is kept at room temperature until the process is complete. This must be done quickly to minimize the warm storage of RBCs in the unit. Blood Here are further guidelines. Medical biochemistry Here are further guidelines. Hospital Blood Transfusion Services Why do people need blood transfusions? 1. Trauma. 2. Surgery. 3. Hematological or oncological medical conditions. Here are further guidelines. Here are further guidelines. |
Cardiovascular Drugs
|
ANTI-ANGINAL DRUGS
Glyceryl Trinitrate Sublingual Tablet, 500 microgram Isosorbide Dinitrate Sublingual Tablet, 5 mg Isosorbide Dinitrate Tablet, 10 mg Nifedipine Tablet, 10 mg (slow release) Nifedipine Tablet, 20 mg (slow release) Nifedipine Tablet, 30mg (GITS) Propranolol Tablet, 10mg Propranolol Tablet, 40 mg Propranolol Tablet, 80 mg ANTIDYSRHYTHMIC DRUGS Amiodarone Tablet, 200mg Disopyramide Capsule, 100mg Disopyramide Phosphate Injection, 10mg/ml Lidocaine Injection, 20 mg/ml in 5 mls Propranolol Tablet, 10mg Propranolol Tablet, 40 mg Propranolol Tablet, 80 mg ANTIHYPERTENSIVE DRUGS Atenolol Tablet, 100 mg Atenolol Tablet, 50 mg Bendroflumethiazide Tablet, 2.5 mg Bendroflumethiazide Tablet, 5 mg Hydralazine Injection, 20 mg Hydralazine Tablet, 25 mg Labetalol Injection, 5 mg/ml Labetalol Tablet, 100 mg Labetalol Tablet, 200 mg Lisinopril Tablet, 2.5 mg Lisinopril Tablet, 5 mg Lisinopril Tablet, 10 mg Losartan Tablet, 25 mg Losartan Tablet, 50 mg Losartan Tablet, 100 mg Methyldopa Tablet, 250 mg Nifedipine Capsule, 10 mg Nifedipine Capsule, 5 mg Nifedipine Tablet, 10 mg (Slow release) Nifedipine Tablet, 20 mg (Slow release) Nifedipine Tablet, 30 mg (GITS) Prazosin Tablet, 500 microgram Propranolol Injection, 1 mg/ml Propranolol Tablet, 10 mg Propranolol Tablet, 40 mg Propranolol Tablet, 80 mg Reserpine Injection, 1 mg/ml Reserpine Tablet, 250 microgram CARDIAC GLYCOSIDES Digoxin Elixir, 50 microgram/ml Digoxin Injection, 250 microgram/ml Digoxin Tablet, 125 microgram Digoxin Tablet, 250 microgram LIPID-REGULATING DRUGS Fluvastatin Capsules, 20mg DRUGS USED IN SHOCK Dopamine Injection, 40 mg/ml in 5 ml Hydrocortisone Injection, 100 mg |
Dermatological Preparations
|
ANTIFUNGAL DRUGS ANTI-INFECTIVE DRUGS ANTI-INFLAMMATORY AND ANTIPRURITIC DRUGS ASTRINGENT AGENTS SCABICIDES AND PEDICULOCIDES EMOLLIENTS OTHERS ANTIFUNGAL DRUGS Benzoic Acid + Salicylic Acid Ointment, 6%+3% Clotrimazole + Hydrocortisone Cream, 2% + 1% Clotrimazole Cream, 2% Clotrimazole Pessary, 100 mg Gentian Violet Paint, 1% Selenium Sulphide Shampoo, 2.5% ANTI-INFECTIVE DRUGS Aciclovir Cream, 5% Cetrimide Solution Chlorhexidine Cream, 1% Chlorhexidine Solution, 2.5% Silver Sulfadiazine Cream, 1% ANTI-INFLAMMATORY AND ANTIPRURITIC DRUGS Calamine Lotion, 15% Calamine Cream, 15% Clobetasol propionate Cream, 0.05% Hydrocortisone Cream, 1% ASTRINGENT AGENTS Salicylic Acid Ointment, 2% SCABICIDES AND PEDICULOCIDES Benzyl Benzoate Lotion, 25% Lindane Lotion, 1% EMOLLIENTS Aqueous Cream BP OTHERS Benzoyl Peroxide Solution, 10% Benzoyl Peroxide Solution, 5% Clindamycin Solution, 1% Mercurochrome Solution |
Drugs Affecting The Blood
|
ANTIANAEMIA DRUGS Iron + Folic Acid Tablet, 60 mg + 250 microgram Ferric Ammonium Citrate (FAC) Ferrous Fumarate Tablet, (100 mg Iron) Ferrous Gluconate Tablet, (35 mg Iron) Ferrous Sulphate (BPC) Syrup, 60 mg/5 ml Ferrous Sulphate Tablet, 60 mg (Elemental Iron) Folic Acid Tablet, 5 mg Hydroxocobalamin Injection, 1 mg/ml Iron Dextran Injection, 50 mg/ml ANTICOAGULANTS AND ANTAGONISTS Acetyl Salicylic Acid Tablet, 75 mg Heparin [Low molecular weight] Injection, 4000 units/ml Heparin Injection, 1000 units/ml Heparin Injection, 5000 units/ml Heparin Injection, 5000 units/0.2 ml Protamine Sulphate Injection, 10mg/ml Phytomenadione Injection, 10 mg/ml Phytomenadione Injection, 1 mg/ml Warfarin Tablet, 1 mg Warfarin Tablet, 3 mg Warfarin Tablet, 5 mg (scored) |
Diagnostic Agents
|
OPHTHALMIC DRUGS Fluorescein Solution, 2% Fluorescein Strips Methylcellulose Eye Drops, 1% Methylcellulose Eye Drops, 2% Rose Bengal Minims, 1% Tropicamide Eye Drops, 1% BED-SIDE DIAGNOSTIC SUPPORT Diagnostic Strips - Glucose Diagnostic Strips - Multipurpose Diagnostic Strips - Protein Diagnostic Tablets - Glucose Diagnostic Tablets - Ketones OTHERS Edrophonium Injection, 10 mg/ml |
Disinfectants
|
Chlorhexidine Solution, 4% in detergent base Chlorhexidine Cream, 1% Chlorhexidine Solution, 2.5% Iodine + Potassium Iodide Solution, 2% + 2.4% Povidone Iodine (aq.) Solution, 10% |
Diuretics
|
Bendroflumethiazide Tablet, 2.5 mg Bendroflumethiazide Tablet, 5 mg Furosemide Injection, 10 mg/ml in 2 ml Furosemide Tablet, 40 mg Mannitol Injection, 10% 500 ml Mannitol Injection, 20% 500 ml Metolazone Tablet, 5 mg Spironolactone Tablet, 25 mg Spironolactone Tablet, 50 mg |
Psychotherapeutic Drugs
|
Amitriptyline Tablet, 10 mg Amitriptyline Tablet, 25 mg Amitiyptyline Tablet, 50 mg Chlorpromazine Injection, 25 mg/ml in 2 mls Chlorpromazine Tablet, 100 mg Chlorpromazine Tablet, 25 mg Chlorpromazine Tablet, 50 mg Diazepam Injection, 5 mg/ml in 2 ml Diazepam Tablet, 10 mg Diazepam Tablet, 5 mg Fluoxetine Capsule, 20 mg Fluphenazine Deconoate Injection, 25 mg/ml Haloperidol Injection, 5 mg/ml Haloperidol Tablet, 10 mg Haloperidol Tablet, 5 mg Imipramine Tablet, 25 mg Lorazepam Tablet, 2.5 mg Risperidone Liquid, 1 mg/ml Risperidone Tablet, 500 microgram Risperidone Tablet, 1mg Risperidone Tablet, 2mg Trifluoperazine Tablet, 1 mg Trifluoperazine Tablet, 5 mg Types of psychotherapeutic agents are: -antianxiety -antimanic -antidepressant -antipsychotic Antidepressants Tricyclic antidepressants Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOI's) Newer generation antidepressants Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRI's) Second and third generation antidepressants Common Tricyclic's Amitriptyline (Elavil) Doxepin (Sinequan) Imipramine (Tofranil) Desipramine (Norpramin) Nortriptyline (Aventyl) Others MAOI's Examples: Nardil and Parnate Newer-Generation Antidepressants Trazodone Wellbutrin SSRI's Paxil Zoloft Celexa Effexor Serzone Remeron Cymbalta Pristiq Lexapro Prozac Antipsychotics Thioxanthenes: Navane Butyrophenones (Haldol) Dihydroindolones (Moban) Phenothiazines Atypical antipsychotics: new class Atypical Antipsychotics Clozaril Risperdal Zyprexa Seroquel Geodon Abilify Invega |
Gastrointestinal Drugs
|
1.ANTACIDS AND OTHER ANTIULCER DRUGS 2.ANTI-EMETICS 3.ANTIHAEMORRHOIDAL DRUGS 4.ANTI-INFLAMMATORY DRUGS 5.ANTISPASMODIC DRUGS 6.CATHARTIC DRUGS 7.DRUGS USED IN DIARRHOEA ANTACIDS AND OTHER ANTIULCER DRUGS Magnesium Trisilicate Mixture Magnesium Trisilicate Tablet, 500 mg Omeprazole Capsule, 20 mg Ranitidine Injection, 25 mg/ml in 2ml Ranitidine Tablet, 150 mg ANTI-EMETICS Metoclopramide Injection, 5 mg/ml in 2 mls Metoclopramide Tablet, 10 mg Ondansetron Injection, 2 mg/ml Ondansetron Tablet, 4 mg Promethazine Hydrochloride Elixir, 5 mg/5 ml Promethazine Hydrochloride Injection, 25 mg/ml Promethazine Theoclate Tablet, 25 mg ANTIHAEMORRHOIDAL DRUGS Ethanolamine Oleate Solution, 5% Phenol 5% in Almond Oil Injection Soothing Agent + Local Anaesthetic Ointment Soothing Agent + Local Anaesthetic Suppository Soothing Agent + Local Anaesthetic + Steroid Ointment Soothing Agent + Local Anaesthetic + Steroid Suppository ANTI-INFLAMMATORY DRUGS Sulfasalazine Tablet, 500 mg ANTISPASMODIC DRUGS Hyoscine Butylbromide Tablet, 10 mg Hyoscine Butylbromide Injection, 20 mg/ml Mebeverine Tablet, 135 mg CATHARTIC DRUGS Bisacodyl Tablet, 5 mg Lactulose Liquid 3.1- - 3.7 g/5 ml Magnesium Sulphate salt Paraffin Liquid Senna Tablet, 7.5 mg or Granules DRUGS USED IN DIARRHOEA Oral Replacement Solution Oral Rehydration Salts Powder Antidiarrhoeal (Symptomatic) Drugs Codeine Tablet, 30mg |
Hormones, Other Endocrine Drugs And Contraceptives
|
ADRENAL HORMONES AND SYNTHETIC SUBSTITUTES Dexamethasone Injection, 4 mg/ml Fludrocortisone Tablet, 100 microgram Hydrocortisone Sodium Succinate Injection, 100 mg Prednisolone Tablet, 5 mg ANDROGENS Testosterone Enanthate Injection, 200 mg in 1 ml ampoule CONTRACEPTIVES Medroxyprogesterone Acetate Injection, 150 mg/ml (Depot) What is medical abortion? A medical abortion is a type of non-surgical abortion in which abortifacient pharmaceutical drugs are used to induce abortion. An oral preparation for medical abortion is commonly referred to as an abortion pill. Total 4 There are two types of abortion treatment, 'Medical' and 'Surgical' abortion: 1. Medical abortion: The abortion pill There are two types of medical abortion Abortion pill (also known as early medical abortion) up to 10 weeks Abortion pill from 10 weeks up to 24 weeks 2. Surgical abortion Surgical abortion involves a quick, minor operation. There are two types of surgical abortion: Vacuum aspiration up to 15 weeks Dilatation and evacuation between 15 and 24 weeks ESTROGENS Conjugated Oestrogen Tablet, 625 microgram Conjugated Oestrogen + Norgesterol Tablet, 625 microgram + 150 microgram Conjugated Oestrogen Vaginal cream, 625 micrograms/g INSULINS AND OTHER ANTIDIABETIC DRUGS Isophane Insulin Injection (HM), 100 units/ml in 10 ml Insulin pre-mixed (30/70) HM Injection, 100 units/ml in 10 ml Insulin Soluble HM, 100 units/ml in 10 ml Glibenclamide Tablet, 5 mg Gliclazide Tablet, 80 mg Tolbutamide Tablet, 500 mg Metformin Tablet, 500 mg Glucagon Injection, 1 mg OVULATION INDUCERS Clomifene Tablet, 50 mg PROGESTOGENS Medroxyprogesterone Acetate Tablet, 5 mg Norethisterone Tablet, 5 mg THYROID HORMONES AND ANTITHYROID DRUGS Carbimazole Tablet, 5 mg Carbimazole Tablet, 20 mg Levothyroxine sodium Tablet, 50 microgram Levothyroxine sodium Tablet, 100 microgram OTHER ENDOCRINOLOGICAL DRUGS Bromocriptine Tablet, 2.5 mg |
Immunologicals
|
DIAGNOSTIC AGENTS Discard Tuberculin (PPD) Injection SERA AND IMMUNOGLOBULINS Anti D Rh Immune Globulin Injection Antirabies immunoglobulins Injection, 1000 IU/5ml Anti-snake venom, Polyvalent Injection Tetanus Immunoglobulins Injection, 250 IU/ml VACCINES BCG Vaccine Injection "Five in One" Vaccine Injection (Diphtheria, Pertussis, Tetanus, Haemophilus influenzae b and Hepatitis B) Hepatitis B Vaccine Injection Measles Vaccine Injection Poliomyelitis Vaccine Oral Solution Tetanus Vaccine Injection, 40 IU/5 ml Yellow Fever Vaccine Injection For Specific Groups of Individuals Meningococcal Vaccine Injection Rabies Vaccine Injection Tetanus Toxoid Injection, 0.5 ml Tetanus Vaccine Injection, 40 IU/5 ml Yellow Fever Vaccine Injection |
Muscle Relaxants And Cholinesterase Inhibitors
|
Atracurium Injection, 10 mg/ml in 2.5 ml
Neostigmine Injection, 2.5 mg Neostigmine Injection, 0.5 mg Rocuronium Injection, 10 mg/ml Suxamethonium Injection, 100 mg/2ml Vecuronium Bromide Injection, 10 mg/vial |
Oxytocics And Anti-Oxytocics
|
OXYTOCICS Ergometrine Injection, 0.5 mg/ml Ergometrine Tablet, 0.5 mg Misoprostol Vaginal Tablet,, 200 microgram Oxytocin Injection, 5 units/ml ANTI-OXYTOCICS Salbutamol Sulphate Injection, 500 microgram/ml Salbutamol Tablet, 4 mg |
Pre-Operative Medications And Sedation For Short-Term Procedures
|
Atropine Injection, 0.6 mg/ml Diazepam Injection, 5 mg/ml Doxapram Injection, 20 mg/ml in 5 ml Ephedrine HCl Injection, 3 mg/ml Glycopyrronium Injection, 200 microgram/ml Lorazepam Injection,4 mg/ml Midazolam Injection, 2 mg/ml Midazolam Injection, 5mg/ml |
Respiratory / Pulmonary Medications
Drugs Acting On The Respiratory Tract
Antiasthmatic Drugs
|
Adrenaline Injection, 1 mg/1ml (1:1000) Aminophylline Injection, 250 mg/10 ml Beclometasone dipropionate Inhaler, 100 mcg/metered dose Beclometasone dipropionate Inhaler, 50 mcg/metered dose Hydrocortisone Sodium Succinate Injection, 100 mg Prednisolone Tablet, 5 mg Salbutamol Inhaler, 100 microgram/metered dose, 200 doses Salbutamol Nebulizer, 2.5 mg Nebules Salbutamol Nebulizer, 5 mg Nebules Salbutamol Syrup, 2 mg/5 ml Salbutamol Tablet, 2 mg Salbutamol Tablet, 4 mg Theophylline Dry Syrup, 60 mg/5 ml Theophylline Tablet, 200 mg (slow release) Antitussives Dihydrocodeine Tablet, 30 mg Simple Linctus (paediatric) Simple Linctus Syrup Respiratory disease Aspiration Pneumonia (43 drugs) Asthma (188 drugs in 6 topics) Berylliosis (6 drugs) Bronchiectasis (46 drugs) Bronchitis (127 drugs) Bronchopleural Fistula (0 drugs) Bronchospasm Prophylaxis (14 drugs) Bronchospastic Disease (0 drugs) COPD (114 drugs in 4 topics) Cough (575 drugs in 2 topics) Croup (19 drugs in 2 topics) Dyspnea (0 drugs) Hiccups (7 drugs) Hypereosinophilic Syndrome (22 drugs in 2 topics) Lymphangioleiomyomatosis (2 drugs) Mechanical Ventilation (0 drugs) Mucous Plugging in Lung Disease (0 drugs) Nasal Congestion (226 drugs) Pleural Effusion (13 drugs in 2 topics) Pleuropulmonary Infection (205 drugs in 5 topics) Pulmonary Fibrosis (8 drugs in 2 topics) Pulmonary Heart or Vascular Disease (36 drugs in 6 topics) Pulmonary Impairment (0 drugs) Respiratory Depression (1 drug) Respiratory Failure (35 drugs in 4 topics) Rhinitis (79 drugs in 3 topics) Upper Respiratory Tract Infection (787 drugs in 7 topics) Vocal Cord Dysfunction (0 drugs) |
Solutions Correcting Water And Electrolyte Abnormalities
|
ORAL PREPARATIONS Oral Rehydration Salts Powder Potassium Chloride Tablet, 600 mg (enteric coated) What are the different type of intravenous fluids for human needs? Types of IV fluids 1. Crystalloids 2. Colloids 3. Blood and blood products PARENTERAL SOLUTIONS Badoe's Solution Injection, 1000 ml Cholera Replacement Fluid Injection, (5:4:1) Darrow's Solution Injection, Half-Strength 250 ml Dextrose in Sodium Chloride Intravenous Infusion, 4.3% in 0.18% 250 ml Dextrose in Sodium Chloride Intravenous Infusion, 5% in 0.9% (500 ml) Dextrose† in Sodium Chloride Intravenous Infusion, 10% in 0.18% (250 ml) Dextrose Infusion, 5% (250 ml) Dextrose Infusion, 5% (500 ml) Dextrose Infusion, 10% (250 ml) Dextrose Infusion, 10% (500 ml) Dextrose Infusion, 20% (250 ml) Dextrose Infusion, 50% (50 ml) Potassium Chloride Injection, 20 mEq/10 ml Ringer’s Lactate Intravenous Infusion, 500 ml Sodium Bicarbonate Injection, 8.4% in 10 ml Sodium Chloride + KCl Injection, 0.9% + 20 mMol (500 ml) Sodium Chloride in Dextrose Injection, 0.9% in 5% (500 ml) Sodium Chloride Injection, 0.9% (250 ml) Sodium Chloride Injection, 0.9% (500 ml) Sodium Chloride Injection, 0.45% (250 ml) MISCELLANEOUS Water for Injection INDICATIONS Rehydration and fluid replacement Replenish Na+ and Cl- Provide energy replacement to protect protein stores (glucose containing solutions) EXAMPLES ISOTONIC Ringer’s, Lactated Ringer’s, 2.5 % Dextrose/Lactated Ringer’s .9% Normal Saline HYPERTONIC 10% Dextrose, 20 % Dextrose, 50% Dextrose 3% Saline, 5% Saline 5% Dextrose/.45% Saline, 5% Dextrose/.9 % Normal Saline, 5% Dextrose/Lactated Ringer’s HYPOTONIC 2.5% Dextrose, 5% Dextrose .45% Saline PRECAUTIONS Hypertonic solutions should be administered slowly as they could cause CHF Monitor flow rate carefully to prevent fluid overload COLLOIDS OVERVIEW Colloids differ from crystalloids in two primary aspects. First, colloids are large particles made up of proteins and second, they are used for rapid expansion of the patient’s intravascular volume. Crystalloids may be used to move fluid forwards and backwards across the cellular membrane. Colloids tend to draw the fluid from the interstitial spaces of the body. A 50 cc container of 25% albumin solution is the equivalent of a 250 cc bolus of fluid. INDICATIONS Rapid replacement of intravascular fluid Hypotension Correct albumin and protein levels EXAMPLES 5 % Albumin 25 % Albumin Plasma protein fraction (5 % albumin and globulin in a solution of normal saline) PRECAUTIONS Due to the extreme osmotic gradient these products produce, be alert for signs of fluid overload (CHF and/or pulmonary edema). PARENTERAL THERAPY OVERVIEW These supplements provide calories, fats, amino acids, and/or electrolytes to the patient that exhibits an impaired gastrointestinal tract or for short term nutritional management. The average daily protein (amino acids) requirements of an adult is approximately 1 gram/kg of body weight. The body requires within the area of 1,600 cal/day for daily maintenance. If the daily caloric intake drops below 400 cal/day, the body begins to use its own source of protein. INDICATIONS Provide calories Spare the body’s protein Maintenance of nutritional status EXAMPLES Amino acids Fat emulsions Total parenteral nutrition (TPN) PRECAUTIONS Fat emulsions are incompatible with electrolyte solutions. Watch for adverse reactions to fat emulsion therapy, such as nausea, vomiting, headache, dyspnea and allergic reactions. Avoid using an in-line filter for the administration of fats Use an IV pump for TPN administration due to the possibility of inducing hyperosmolality Due to the high glucose content of TPN (and subsequently the chance for bacterial growth), sterile technique is called for when changing IV bag solutions. Glucose intolerance may occur with TPN administration due to the inability of the pancreas to handle the extra sugar load. Generally this occurs at the onset of treatment; however, close monitoring of the patient’s glucose level is necessary. If the patient is found to be glucose intolerant insulin will be added to the mixture. TYPE OF BLOOD PRODUCTS Common Packed red blood cells Erythrocytes and 100 ml of plasma Platelets Plasma volume of 50 ml Fresh frozen plasma Volume of 200 to 250 ml, contains all coagulation factors, but no platelets Whole blood Volume of 500 ml, missing factors VII and V, no platelets Uncommon Cryoprecipitate Plasma volume of 10 to 25 ml including factor VIII and fibrinogen Clotting factors Vaccines Top 10 Vaccine-Preventable Diseases 1. Measles 2. Whooping Cough (Pertussis) 3. Flu 4. Polio 5. Pneumococcal Disease 6. Tetanus 7. Meningococcal Disease 8. Hepatitis B 9. Mumps 10. Hib (Haemophilus Influenzae Type B) Measles What it is: A highly contagious lung infection. The measles virus gets into the air when someone who has it coughs or sneezes Whooping Cough (Pertussis) What it is: A lung infection that makes it hard to breathe due to severe coughing. People can breathe in the pertussis bacteria when someone who has whooping cough coughs or sneezes. Flu What it is: A viral infection of the nose, lungs, and throat. Polio What it is: A viral disease How you get it: The polio virus lives in the intestines. You can get infected by coming into contact with a sick person’s feces. Pneumococcal Disease What it is: A bacterial disease that can cause many types of illness, including pneumonia, ear and blood infections, and meningitis (which affects the brain and spinal cord). How you get it: By coming into contact with an infected person’s mucus or saliva. Tetanus What it is: A bacterial disease that causes lockjaw, breathing problems, muscle spasms, paralysis, and death. Meningococcal Disease What it is: A bacterial disease that can cause meningitis, an infection and swelling of the brain and spinal cord. It can also infect the blood. Hepatitis B What it is: A liver disease caused by the hepatitis B virus. Mumps What it is: A disease caused by a virus that gives people swollen salivary glands, a fever, headache, and muscle aches. It also makes you feel tired and curbs your appetite. Hib (Haemophilus Influenzae Type B) What it is: A bacterial disease that infects the lungs (pneumonia), brain or spinal cord (meningitis), blood, bone, or joints. Vaccines Here are further guidelines. Here are further guidelines. |
Preferred Drug List
|
What is a preferred drug list? If you go through a textbook of pharmacology, pharmacy, or any medical specialty, not all the drugs listed are available in the state. Every state maintains a preferred drug list. The state department of health or state department of health and family services issues a preferred drug list regularly. You need to write to the nearest pharmacy and state department of health. The nearest pharmacy can be a hospital or non-hospital pharmacy. Can you bring me up to date with a preferred drug list? Are these preferred drug lists available in nearest pharmacy? You need to reach a correct diagnosis before prescribing any drug in the preferred drug list. What is an essential drug list? A state on January 13, 2012, has listed 348 essential drugs that can tackle not only critical cases but almost all medical conditions. What do you need to answer? Questions you need to answer. What drugs or medications are in the essential list of drugs or preferred list of drugs from pharmaceutical factories in the state? What are the drugs from pharmaceutical factories outside the state? Why can't drugs from pharmaceutical factories outside the state be manufactured within the state? |
| Here are further guidelines. |
Where do they work?
|
