| Admissions | Aircraft | Aviation World | Ambassadors | Accreditation | A to Z Degree Fields | Books | Catalog | Colleges | Contact Us | Continents/States | Construction | Contracts | Distance Education | Emergency | Emergency Medicine | Examinations | English Editing Service | Economy and budget | Forms | Faculty | Governor | Grants | Hostels | Honorary Doctorate degree | Human Services | Human Resources | Internet | Investment | Instructors | Internship | Login | Lecture | Librarians | Languages | Manufacturing | Membership | Observers | Products | Public Health | Publication | Professional Examinations | Programs | Professions | Progress Report | Recommendations | Ration food and supplies | Research Grants | Researchers | Services | Students login | School | Search | Software | Seminar | Study Center/Centre | Sponsorship | Tutoring | Thesis | Universities | Work counseling |
Engine: Including Block, Heads, Pistons & Valves
| Automobile Engines | ||
| Air–fuel ratio | ||
| Horsepower | ||
| Car Materials | ||
Basic Engine Parts
Valves Piston Piston rings The Block Cylinder Head Valve Operating Systems(Cam Shaft) Valve Operating Systems(Tappets/Lifters) Valve Operating Systems(Push Rods) Valve Operating Systems(Rocker Arm) Valve Operating Systems(Valve Springs) Connecting rod Crankshaft Sump Here are further guidelines. | ||
Engine Problems
Lack of compression Lack of spark Here are further guidelines. | ||
|
Engine configurations Internal combustion engines can be classified by their configuration. Common layouts of engines are: Reciprocating:
Four-stroke engine (Otto cycle) Six-stroke engine Diesel engine Atkinson cycle Miller cycle
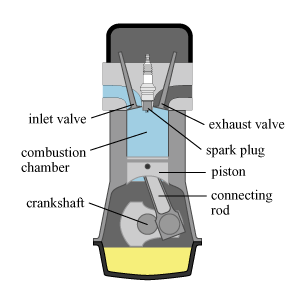
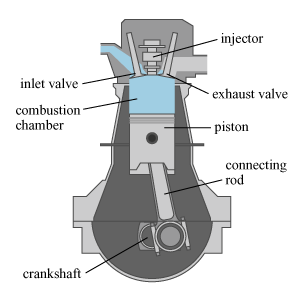
Jet engine (including turbojet, turbofan, ramjet, Rocket, etc.) Most vehicles on the road are powered by internal combustion engines. The most common internal combustion engines for vehicles are fuelled with petrol or diesel. Petrol and diesel engines There are two main differences between the design of a petrol engine and a diesel engine. First, petrol engines use spark ignition while diesel engines use compression ignition. Inside an engine, fuel is burned to release and convert the chemical energy to kinetic energy. In a petrol engine (Fig. 3), a spark plug produces sparks to ignite the mixture of petrol and air. In a diesel engine (Fig. 4), air is compressed to a high temperature so that when a fine mist of diesel is pumped into the compressed air, the intense heat causes the diesel to ignite. This is why diesel engine is called a compression ignition engine.
The second difference is the range of compression ratios of the engines (see the animations below to understand the meaning of "compression ratio"). Diesel engines are designed to operate at higher compression ratios, usually between 15 to 20, while petrol engines have lower compression ratios usually between 8 to 10.Since the higher the compression ratio of an engine the higher the thermal efficiency, so diesel engines generally have a better fuel efficiency than petrol engines. To power a similar sized vehicle, a diesel engine will be about 15% - 25 % better on fuel efficiency than a petrol engine. But diesel engines also have disadvantages. Although diesel engines are more energy efficient, they produce significantly more particulates in the exhaust gas than petrol engines. Diesel engines are also slightly noisier and less refined. To withstand the high compression ratio, diesel engines are more expensive to produce. These factors make diesel engines more suitable for commercial vehicles, because these vehicles usually cover longer distances each day, making diesel engines' fuel efficiency advantage important. | ||
| Petrol engine/gasoline engine | ||

| ||
| How Car Engines Work (Petrol engine/gasoline engine) | ||
| Car Engine Quiz (Petrol engine/gasoline engine | ||
| Diesel Engine Quiz | ||
Car Engine Weight
Calculate The Weight of Your Car for the Engine Size The minimum weight of your car should be 3,900 pounds with an engine size of 600 CID | ||
Engine Questions and Answers
What is the difference between a two-stroke and a four-stroke engine? Are there any other cycles besides the Otto cycle used in car engines? How are 4-cylinder and V6 engines different? Why have eight cylinders in an engine? Why not have one big cylinder of the same displacement of the eight cylinders instead? What does 2.4 liter mean in the context of an engine? How do exhaust headers work to improve engine performance? What's the best way to increase an engine's power? Here are further guidelines. | ||