Equipment Specialist


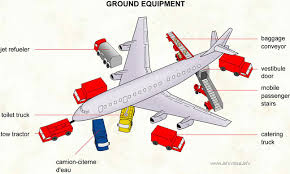




Examples of equipment include devices, machines, tools, and vehicles. |
| Devices |
| Machines |
| Tools |
| Vehicles |
|
What is professional equipment? Tools, machines, or other things that are needed for a particular job/work/profession. What should you know about professional equipment? Professional equipment includes computers in various departments in the state, helicopters, fighter jets, administrative cars, ships, weapons, law enforcement equipment, health care equipment, and equipment relevant to other professions. |
|
Equipment may refer to: |
| Automation Equipment (Robotic) |
| Aviation Communication equipment |
| Aviation ground support equipment |
| Aircraft Equipment |
| Agricultural equipment |
| Automotive Equipment (Car Workshop Equipment) |
| Audio equipment |
| Cleaning Equipment |
| Car Wash Equipment |
| Construction Equipment |
| Critical care unit equipment |
| Camping equipment |
| Communications Equipment |
|
Data Processing Equipment: Bridges, Controller Cards, Hubs / Switches, Mainframes, Multiplexors, PC’s & Peripherals, Routers, Servers, Tape Drives
Here are further guidelines. |
| Diving equipment |
|
Economy and budget Equipment: Calculators, Computers and Internet, Cards(Illinois link card, etc) Here are further guidelines. |
| Electrical equipment |
| Electrician equipment |
| ER Equipment |
| Engineering equipment |
| Emergency vehicle equipment |
| Electrical equipment |
| Food Equipment |
| Fire apparatus |
| HVAC |
| Home Appliance |
| Hand Tools |
| Heavy equipment (construction) |
| Infantry Gear |
| List of agricultural equipment |
| Laboratory equipment |
| Mobility Equipment |
| Medical Equipment |
|
Mail Equipment: Bag Tagging Equipment, Bar-coding Equipment, Binding Machines, Bursters / Cutters, Collators / Decollators, Conveyers, Sorters, Folders / Inserters, Ink Jet Addressing, Ink Jet Drying, Inserter System, Labeling System
Here are further guidelines. |
| Measuring instruments |
| Medical Equipment |
| Military equipment |
| Materiel |
| Nonessential Equipment and Furnishings |
|
Office Equipment: Collating Machines, Copiers, Dictation Equipment, Endorsers, Fax Machines, Mail Machines, Microfiche / Microfilmers, Plotters, Printers, Rotary Filing Systems, Shredders, Time Clocks, Typewriters, Word Processors
Here are further guidelines. |
| Police Equipment |
| Personal protective equipment |
| Plumbing Equipment |
| Pressure measurement |
| Pump & Valve control |
|
Security Equipment: Alarm Systems, Card Access Systems, Video Surveillance, Vaults & Safes
Here are further guidelines. |
| Ship Equipment |
| Self-propelled passenger equipment |
| Scribe equipment (hieroglyph) |
| School Supplies |
| Scuba set |
| Scientific instruments |
| Tools |
| Telecommunications equipment |
| Vox (musical equipment) |
| Weight Training Equipment |
|
This series includes positions that involve supervision or performance of work that requires
primarily an intensive, practical knowledge of equipment and its characteristics, properties, and
uses in order to (1) collect, analyze, interpret, and provide specialized information about
equipment together with related advice to those who design, test, produce, procure, supply,
operate, repair, or dispose of equipment; (2) identify and recommend practical solutions to
engineering design and manufacturing defects and recommend use of substitute testing or support
equipment when the equipment requested is unavailable; or (3) develop, install, inspect, or revise
equipment maintenance programs and techniques.
Equipment Specialist GLOSSARY OF TERMS ITEM - A word used to indicate a piece of equipment where distinguishing between a part, subassembly, etc., is not important to the context; PART - A unit consisting of one or two items of equipment usually not capable of being disassembled without destruction; SUBASSEMBLY - A unit consisting of two or more parts that form a portion of an assembly or component. It is replaceable as a whole and may have parts that are individually replaceable; ASSEMBLY - A unit consisting of several parts and subassemblies joined to perform a specific function; e.g., an electric switch unique to a submarine; COMPONENT - A unit consisting of a combination of parts, subassemblies, and assemblies mounted together that is normally capable of action in a number of situations, e.g., a complete unit such as a pump, motor, governor, or turbine; SUBSYSTEM - A unit consisting of a combination of parts, subassemblies, assemblies, and components connected to perform an operational function, e.g., an airframe, a complete propulsion unit of an aircraft, a motor vehicle drive train, a guidance or propulsion unit of a spacecraft, or a ground support radar system; SYSTEM - A unit consisting of a combination of parts, subassemblies, assemblies, components, and subsystems associated together to form a complete aircraft, missile, machine, motor vehicle, or weapon; COMMODITY CLASS - Items of equipment grouped together for inventory identification because they have similar characteristics, e.g., a group of hydraulic pumps and motors, or a ________ supply class or group of items. The equipment specialist occupation includes a wide range of work and work settings. The primary distinguishing features are that the nature of the work requires application of an intensive, practical knowledge of equipment and its characteristics, properties, and uses; and that this knowledge is more important in the recruitment and selection process and in performance of the work than other required qualifications. Here are further guidelines. |
