
Airplane Parts & Functions
-
Aircraft Batteries
-
Aircraft Stairs
-
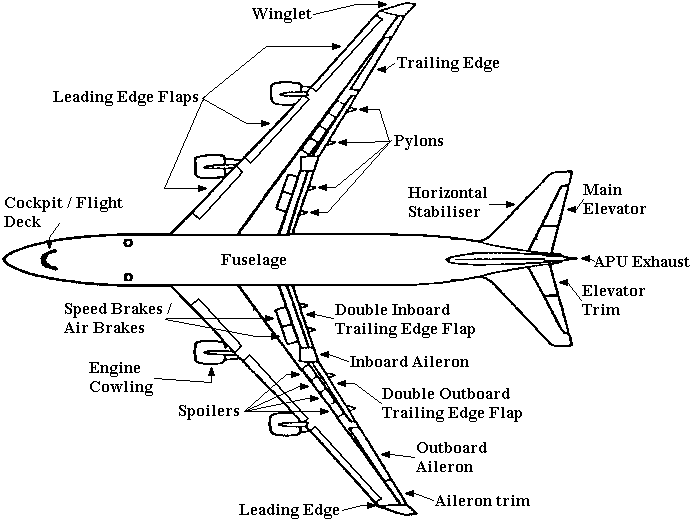
Aileron Trim: To roll left & right a little.
-
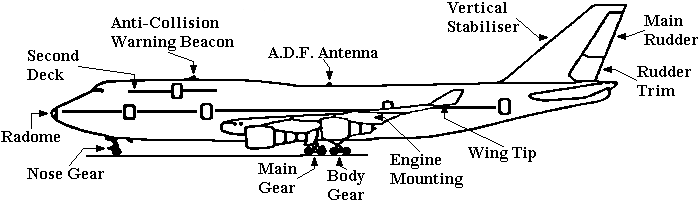
Anti-Collision Warning Beacon: A red light to warn other aircraft and help prevent mid-air collisions.
-
Aircraft cabin
-
Aircraft lavatory
-
Aircraft weapons
-
Airplane Wings
-
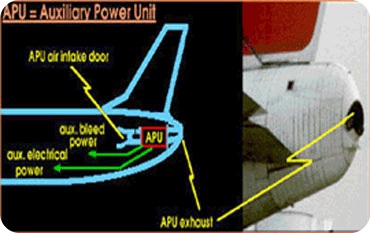
A.P.U. Exhaust: This is the exhaust pipe for the A.P.U. (Auxiliary Power Unit). The A.P.U. is an engine in the tail of the aircraft. It is used only on the ground. It generates electrical power for the aircraft and is used to start the jet engines.
-
Cockpit / Flight Deck: In this room, pilots aviate, communicate, and navigate.
-
Door
-
Elevator
-
Elevator Trim: To pitch up & down a little.
-
Engine Cowling: The main cover or housing of the engine.
-
Engine Mounting: Used to fix the engine to the wing.
-
Environmental control system (aircraft)
-
Fin and Dorsal
-
Flap: To increase lift during take-off and landing. Pilots extend the flaps to increase the wing's area. This increases the lift.
-
Fuselage: The body or structure of the aircraft.
-
Horizontal Stabiliser: Stabilises the aircraft around the lateral axis.
-
Landing Gear: Pilots extend or retract the landing gear (wheels) during take-off and landing.
-
Landing Light
-
Left Wing Aileron
-
Left Wing Flap
-
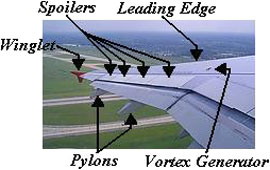
Leading Edge: Front section of the wing.
-
Main Elevator: To pitch up & down.
-
Main Rudder: To yaw (turn) left & right.
-
Nose Gear: The front wheels of the aircraft. Aircraft also have MAIN GEAR (wheels under the aircraft's wings) and sometimes BODY GEAR (wheels under the aircraft's body).
-
Passenger service unit
-
Propeller: Gives an aircraft thrust or power.
-
Pylons: Used to stabilise the air flow behind the wing. Without pylons, the air is unstable. This makes drag, and reduces the aircraft's speed and performance.
-
Radome: The aircraft's radar is inside the radome or nose of the aircraft.
-
Right Wing Aileron
-
Right Wing Flap
-
Rudder
-
Rudder Trim: To yaw left & right a little.
-
Seat
-
Speed Brakes / Air Brakes: Used to slow the plane in the air and while landing.
-
Spoilers: Used to destroy lift and keep the plane on the ground. This is important while landing. Without spoilers, the plane bounces on the runway. This can damage the landing gear. Some pilots prefer hard landings to help prevent bounce.
-
Spinner
-
Stabiliser Trim: To increase the angle of attack (A.O.A.). Basically, the angle of attack is the angle the wing hits the air.
-
Trailing Edge: Back section of the wing.
-
Vertical Stabiliser: Stabilises the aircraft around the vertical axis.
-
Vortex Generator: Used to create lift in areas of the wing that have no or very little lift, for example, next to the engine mounting.
-
Wheel Cover
-
Windshield
-
Wing Strut
-
Wing Tip Light
-
Winglet: Used to reduce the vortex at the end of the wing. A vortex is unstable circular air. It makes drag, and reduces the aircraft's speed and performance.
-
Wing Tip: The end or tip of the wing.
|
As opposed to jet airplanes, which are propelled via jet engines, many aircraft make use of propellers, which slice through the air to create thrust. Within an air mass, airplane propellers move in a motion that is similar to that of a corkscrew – what is called a helical motion.
Aircraft such as the ATR 72, Tupolev Tu-95, and Bombardier Dash 8 use a system that incorporates propellers powered by engines that are equipped with turbochargers (i.e exhaust gas-driven superchargers), and are hence often referred to as “turboprops.” Other aircraft, such as the common single-engine Cessna – 172 use a simple propeller assembly. In this case, the airplane propeller is mounted onto a crankshaft connected to the engine.

A C-130 Super Hercules with scimitar propellers providing thrust for take-off.
Jet aircraft
A jet aircraft (or simply jet) is an aircraft (nearly always a fixed-wing aircraft) propelled by jet engines.
Jet engine
Uses
Jet engines power aircraft, cruise missiles and unmanned aerial vehicles. In the form of rocket engines they power fireworks, model rocketry, spaceflight, and military missiles.
Types
Airbreathing
Turbine powered
Turbojet
Turbofan
Turboprop and turboshaft
Propfan
Ram powered
Ramjet
Scramjet
Non-continuous combustion
Rocket
Hybrid
Water jet
|






